Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Maekawa, Fujio; Oikawa, Kenichi; Harada, Masahide; Kai, Tetsuya; Meigo, Shinichiro; Kasugai, Yoshimi; Oi, Motoki; Sakai, Kenji; Teshigawara, Makoto; Hasegawa, Shoichi; et al.
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 600(1), p.335 - 337, 2009/02
Times Cited Count:42 Percentile:92.82(Instruments & Instrumentation)A neutron beam line (BL10) of JSNS, NOBORU, has been constructed in the Materials and Life Science Experimental Facility (MLF) at J-PARC. A primal mission of NOBORU is to study neutronic performance of JSNS. We will measure the memorable first neutron pulse of JSNS at the Day-one by using NOBORU, and then measure neutron pulse shape, spectrum, intensity distribution, etc. for facility diagnostics. Since NOBORU also has an aspect as a test port, it welcomes trial uses to develop innovative instruments. Trial experiments to demonstrate several innovative instruments at NOBORU are under planning.
Takahashi, Nobuaki; Shibata, Kaoru; Sato, Taku*; Kawakita, Yukinobu*; Tsukushi, Itaru*; Metoki, Naoto; Nakajima, Kenji; Arai, Masatoshi
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 600(1), p.91 - 93, 2009/02
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:50.49(Instruments & Instrumentation)A time-of-flight crystal-analyzer neutron inelastic scattering spectrometer DNA has been proposed to construct in the MLF of J-PARC. DNA has been designed to have three crystal analyzers, PG(002), Ge(311) and Si(111) at near-backscattering configurations to study dynamics of biomolecules and proteins in wide energy and momentum transfer ranges. In order to develop the Ge(311) analyzer-crystals we have performed neutron beam experiments to check rocking curves on two candidates, i.e., (a) thick hot-pressed wafers and (b) stacked number of thin as-cut wafers, at the MUSASI port, which is a triple-axis instrument, located on the T2 beam line at the JRR-3M guide hall, Tokai, Japan.
Oi, Motoki; Kai, Tetsuya; Kinoshita, Hidetaka; Sakai, Kenji; Kaminaga, Masanori; Futakawa, Masatoshi
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 600(1), p.120 - 122, 2009/02
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:12.35(Instruments & Instrumentation)The Materials and Life Science Experimental Facility (MLF) of J-PARC has the general control system (MLF-GCS) that controls all subsystems of the MLFAccording to classifying into each function, the MLF-GCS consists of three layers of a PLC (programmable logic controller) link layer, server layer and external network layer. The PLC link layer is an inner layer and core part of the MLF-GCS. The server layer acquires various data from the inner and outer layer. The server systems also protect the core part of the MLF-GCS from network troubles of external LANs by mediating between the inner and outer layer. The server systems play an important role for realizing advanced and independent control in the MLF. A modeling and construction of the server systems have been almost finished, and an improvement and optimization of them are now in progress. This paper gives an overview of the server systems for the MLF-GCS and reports on their development status.
Harada, Masahide; Meigo, Shinichiro; Ito, Manabu; Dantsuji, Eiji; Takagiwa, Katsunori; Takada, Hiroshi; Maekawa, Fujio; Futakawa, Masatoshi; Nakamura, Mitsutaka; Miyake, Yasuhiro*; et al.
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 600(1), p.87 - 90, 2009/02
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:28.2(Instruments & Instrumentation)In MLF of J-PARC, since weights of a building and shields are considerably heavy as 130,000 tons and 80,000 tons, respectively, large settlement of the MLF building is expected. The 3NBT line with 300 m in length is similar. To achieve a precise alignment under the large settlement, we conducted periodical survey measurements at the MLF building and 3NBT. At the completion of construction of the MLF building in December 2005, the settlement was about 40 mm. By extrapolating this result with weights to be added in the future for neutron beam line shields, we predicted that the MLF building settled in about 68mm at the completion of all neutron instrument construction. We decided that the muon target should be installed 5 mm higher than the neutron target with expecting future uneven settlement of the MLF building. The validation in the end of 2007 indicated that the measured level difference came up to the expected value.
Haga, Katsuhiro; Kogawa, Hiroyuki; Wakui, Takashi; Naoe, Takashi; Futakawa, Masatoshi; Yamazaki, Shogo*; Tanaka, Nobuatsu*
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 600(1), p.64 - 67, 2009/02
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:21.05(Instruments & Instrumentation)Pitting damage on the target vessel wall caused by the pressure wave is one of the crucial issues to realize a pulsed high-power mercury target for spallation neutron sources. Micro-bubbles injection into mercury is one of prospective technologies to mitigate the pressure waves. As one of the studies for bubbling system design for pitting damage mitigation, preliminary simulation of bubble flow field in the actual target vessel was carried out and the optimal condition of bubble injection was investigated. The simulations were carried out with FLUENT. In two dimensional simulations, the bubbles of 50  m diameter could be carried more than 2000 mm, which corresponds to the length of the target vessel, with small rising height. Then three dimensional simulations were carried out for the case of the bubble diameter of 50
m diameter could be carried more than 2000 mm, which corresponds to the length of the target vessel, with small rising height. Then three dimensional simulations were carried out for the case of the bubble diameter of 50  m and 500
m and 500  m. As results, we could have prospect that bubbles are distributed to the desirable regions when they are injected in proper position according to the bubble diameter.
m. As results, we could have prospect that bubbles are distributed to the desirable regions when they are injected in proper position according to the bubble diameter.
 Li
Li TaO
TaO
Wakimoto, Shuichi; Samara, G. A.*; Grubbs, R. K.*; Venturini, E. L.*; Boatner, L. A.*
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 600(1), p.254 - 256, 2009/02
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:28.2(Instruments & Instrumentation)Neutron scattering experiments have been performed on relaxor ferroelectric K Li
Li TaO
TaO with
with  =0.05 and 0.10, where the former shows only relaxor behavior down to the lowest temperature, and the latter shows ferroelectric phase transition in addition to the relaxor behavior at higher temperatures. Studies of ferroelectric (FE) soft mode and diffuse scattering from the polarized nano-regions revealed that the FE soft mode behaves as similar as that in conventional displacive ferroelectrics. Also, it is found that the displacements of atoms in the polarized nano-regions contains a component which results from a condensation of the ferroelectric mode and a uniform displacements of all atoms. These facts suggest that the zone-center ferroelectric mode has an important contribution to the ferroelectric behavior in this system in addition to the Li atoms dipole relaxation.
=0.05 and 0.10, where the former shows only relaxor behavior down to the lowest temperature, and the latter shows ferroelectric phase transition in addition to the relaxor behavior at higher temperatures. Studies of ferroelectric (FE) soft mode and diffuse scattering from the polarized nano-regions revealed that the FE soft mode behaves as similar as that in conventional displacive ferroelectrics. Also, it is found that the displacements of atoms in the polarized nano-regions contains a component which results from a condensation of the ferroelectric mode and a uniform displacements of all atoms. These facts suggest that the zone-center ferroelectric mode has an important contribution to the ferroelectric behavior in this system in addition to the Li atoms dipole relaxation.
Utsumi, Wataru; Kagi, Hiroyuki*; Komatsu, Kazuki*; Arima, Hiroshi*; Nagai, Takaya*; Okuchi, Takuo*; Kamiyama, Takashi*; Uwatoko, Yoshiya*; Matsubayashi, Kazuyuki*; Yagi, Takehiko*
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 600(1), p.50 - 52, 2009/02
Times Cited Count:13 Percentile:64.65(Instruments & Instrumentation)The application of high pressure can induce dramatic changes in the physical properties of condensed matter. Diffraction experiments under high pressure provide precise structural information, which is fundamental to understand their origin. When in situ high pressure neutron diffraction becomes possible at J-PARC, further outstanding researches are expected such as crystal structure of hydrogen-bearing materials including hydrous minerals, order-disorder transitions of minerals, structure of light element liquid at high pressure, etc.. Conceptual designs of neutron optics and high pressure devices for J-PARC are introduced.
Kajimoto, Ryoichi; Nakajima, Kenji; Nakamura, Mitsutaka; Soyama, Kazuhiko; Yokoo, Tetsuya*; Oikawa, Kenichi; Arai, Masatoshi
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 600(1), p.185 - 188, 2009/02
Times Cited Count:12 Percentile:62.2(Instruments & Instrumentation)no abstracts in English
Sakai, Kenji; Oi, Motoki; Kai, Tetsuya; Kinoshita, Hidetaka; Kawasaki, Susumu; Watanabe, Akihiko; Kaminaga, Masanori; Futakawa, Masatoshi
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 600(1), p.75 - 77, 2009/02
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:12.35(Instruments & Instrumentation)In order to operate all equipment of the Materials and Life Science Experimental Facility (MLF) safely and efficiently, the MLF general control system (MLF-GCS) is designed to have several subsystems such as the facility control system centering on the control of the targets, interlock systems for protecting personnel, machine and the neutron target, and so on. Although it is an independent system, the MLF-GCS should also be as a part of the control system of the whole J-PARC operated from the central control room (CCR). The construction of MLF-GCS has been almost finished, and its performance test is in progress to check and adjust remote operations and integral interlocks from the control room of MLF. This paper gives an overview of the MLF-GCS and reports its construction status.
 SR project at J-PARC MUSE
SR project at J-PARC MUSEHigemoto, Wataru; Heffner, R. H.; Shimomura, Koichiro*; Nishiyama, Kusuo*; Miyake, Yasuhiro*
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 600(1), p.182 - 184, 2009/02
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:12.35(Instruments & Instrumentation)At the J-PARC MLF muon science facility (MUSE), JAEA-ASRC is advancing the " SR project". In this project, the muon beam extraction part and the spectrometer will be installed to the downstream of the Decay/Surface muon beam line as a branch of the beam line. ASRC beam line is preparing for a muon spin rotation and relaxation (
SR project". In this project, the muon beam extraction part and the spectrometer will be installed to the downstream of the Decay/Surface muon beam line as a branch of the beam line. ASRC beam line is preparing for a muon spin rotation and relaxation ( SR) experiment. Mainly, a positive surface muon beam (29MeV/c) will be used for the experiment. One of the main subject of the ASRC
SR) experiment. Mainly, a positive surface muon beam (29MeV/c) will be used for the experiment. One of the main subject of the ASRC  SR project is study of strongly correlated electron systems, especially f-electron systems. By using intense muon beam of MUSE, new insights for f-electron physics will be obtained.
SR project is study of strongly correlated electron systems, especially f-electron systems. By using intense muon beam of MUSE, new insights for f-electron physics will be obtained.
Maruyama, Ryuji; Yamazaki, Dai; Ebisawa, Toru*; Soyama, Kazuhiko
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 600(1), p.68 - 70, 2009/02
Times Cited Count:31 Percentile:87.86(Instruments & Instrumentation)Neutron supermirrors have been utilized as reflective optical devices at many neutron sources for transporting, focusing, polarizing neutron beam. In order to produce such devices for the new spallation neutron source (Japan Proton Accelerator Research Complex, J-PARC), an ion beam sputtering system with an effective deposition area of 0.2 m has been installed in the Japan Atomic Energy Agency. The fabrication methods and the performance of the supermirrors are discussed.
has been installed in the Japan Atomic Energy Agency. The fabrication methods and the performance of the supermirrors are discussed.
Ikeda, Yujiro
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 600(1), p.1 - 4, 2009/02
Times Cited Count:44 Percentile:93.42(Instruments & Instrumentation)Fukazawa, Hiroshi; Hoshikawa, Akinori*; Chakoumakos, B. C.*; Fernandez-Baca, J. A.*
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 600(1), p.279 - 281, 2009/02
Times Cited Count:12 Percentile:62.2(Instruments & Instrumentation)We measured time-resolved neutron powder diffraction of ices doped with very small amounts of some catalysts using the wide-angle neutron diffractometer (WAND) at the High Flax Isotope Reactor (HFIR) in Oak Ridge, Tennessee. We succeeded in making ferroelectric ice, which prepared at high pressures (0.2 and 0.4 GPa), in a 60 to 75 K temperature range over tens hours. Neutron diffraction experiments confirmed the existence of a large ferroelectric structure in the sample. Therefore, thick surface (about 500 Km) of ferroelectric ice may exist on cold icy bodies, such as, Pluto and Kuiper Belt Objects (KBO). It suggests that about 70% of Pluto body is ferroelectric ice. Future telescope or planetary probe will be able to detect the huge ferroelectric-ice mass. In this symposium we report recent results at the HFIR and our future plan using higher intensity neutron beam.
Oikawa, Kenichi; Takada, Hiroshi; Maekawa, Fujio; Harada, Masahide; Futakawa, Masatoshi; Ikeda, Yujiro
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 600, p.84 - 86, 2009/02
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Instruments & Instrumentation)Neutron beam shutter system of JSNS at J-PARC has been designed under a particular precondition that every shutter should be controlled and maintained independently. This is very important from viewpoints of usability and interlock system of JSNS. The biggest challenge we faced was that to meet a single shutter design on asymmetric and narrow angular intervals of JSNS beam-lines; 6.7 in minimum and 12.7
in minimum and 12.7 in maximum. To realize this precondition, a compact ball screw jack system sustaining a shutter gate with two shafts was designed. Rotating motion during open/close stroke is absorbed by a couple of oilless bearings (OILES corp.) fitted in every shaft guide. The assembly is driven by an electric servomotor.
in maximum. To realize this precondition, a compact ball screw jack system sustaining a shutter gate with two shafts was designed. Rotating motion during open/close stroke is absorbed by a couple of oilless bearings (OILES corp.) fitted in every shaft guide. The assembly is driven by an electric servomotor.
Futakawa, Masatoshi; Haga, Katsuhiro; Wakui, Takashi; Kogawa, Hiroyuki; Naoe, Takashi
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 600(1), p.18 - 21, 2009/02
Times Cited Count:19 Percentile:76.04(Instruments & Instrumentation)Pressure waves, which are caused by the thermal shock in mercury at the moment when high intense proton beams bombard mercury, are a crucial issue to realize a pulsed high-power mercury target for spallation neutron sources. R&D on pressure wave mitigation technologies is carried out in JSNS. Based on the R&D results we have carried out so far, the preliminary conceptional design of mercury target was considered.
Kogawa, Hiroyuki; Haga, Katsuhiro; Wakui, Takashi; Futakawa, Masatoshi
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 600(1), p.97 - 99, 2009/02
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:39.08(Instruments & Instrumentation)Mercury circulation system provides mercury into a mercury target for the Japan neutron spallation source (JSNS). A mercury pump in the system circulates mercury to remove heat generated in the mercury target by 1 MW proton beam injection. For stable operation of the system, leak of the activated mercury must be avoided. The induction pump is seal-less however it generally becomes large to get high performance. Furthermore, heat loss in the duct wall occurs and it becomes a heat load to the system. Therefore, a permanent magnet rotating type induction pump (PM pump) was developed. In this pump, the mercury duct was made in circular shape and rotating permanent magnets were installed in the center of the duct to apply the Lorentz force, and a motor to rotate the magnets was vertically set on the top of the pump to make the PM pump compact. And the motor power was limited up to 90 kW to avoid overheat due to heat loss in the pump. The duct size and the thickness of the duct wall were optimized to be able to circulate mercury by 90 kW-motor. Consequently, the PM pump could be set in the mercury circulation system and provided the sufficient mercury to the mercury target.
Tatsumoto, Hideki; Aso, Tomokazu; Kato, Takashi; Otsu, Kiichi; Hasegawa, Shoichi; Maekawa, Fujio; Futakawa, Masatoshi
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 600(1), p.269 - 271, 2009/02
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:12.35(Instruments & Instrumentation)As one of the main experimental facilities in J-PARC, an intense spallation neutron source (JSNS) driven by a 1-MW proton beam selected supercritical hydrogen at the temperature of 20 K and the pressure of 1.5 MPa as a moderator material. A cryogenic hydrogen system plays a role in cooling the moderators. For safety reasons, we have designed a hydrogen relief system that can release hydrogen to the outside safely, even if some off-normal events occur. The design of the hydrogen vent line should be considered to prevent the cryogenic hydrogen from freezing purge nitrogen gas in the vent line and freezing moisture in the stack placed in an outdoor location, and to inhibit the piping temperature drop at the building wall penetration. In this work, the temperature change behaviors in the hydrogen vent line were analyzed by using a CFD code, STAR-CD. We determined the required sizes of the vent line based on the analytical results and its layout in the building.
Shamoto, Shinichi; Kodama, Katsuaki; Iikubo, Satoshi; Taguchi, Tomitsugu
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 600(1), p.229 - 231, 2009/02
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:12.35(Instruments & Instrumentation)As one of scientific research targets at total scattering diffractometers at J-PARC, we propose disordered crystalline functional materials. They are optical recording material, thermoelectric material, relaxor ferroelectric material, and so on. In an optical recording material, a metal-like phase should have low thermal conductivity and high electrical resistivity, simultaneously. This contradicting condition challenges material scientists to design the good functional material, which should have at least two types of crystallographic sites. One site limits the thermal conductivity, whereas the other site carries electrons or holes with high mobility. The periodic boundary condition is lost in the disorder parts. Therefore, the atomic pair distribution function (PDF) analysis is suitable to investigate the form and size of the crystalline parts as well as the disordered parts in the materials.
Higemoto, Wataru; Shimomura, Koichiro*; Kobayashi, Yasuo*; Makimura, Shunsuke*; Miyake, Yasuhiro*; Kai, Tetsuya; Sakai, Kenji
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 600(1), p.179 - 181, 2009/02
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Instruments & Instrumentation)At the J-PARC MLF muon science facility (MUSE), muon experimental instruments are operated by means of a Muon Control System. The following are subject to the Muon Control System: (1) Muon production target and the beam scrapers, (2) M1/M2 line air-conditioning system, (3) Cryogenic system for the superconducting solenoid magnet, (4) Muon secondary line vacuum system, (5) Muon secondary line magnets, and (6) Muon beam blockers and related safety instruments. Details of the muon control system are described.
Matsushita, Yoshitaka*; Izumi, Fujio*; Kobayashi, Kiyoshi*; Igawa, Naoki; Kitazawa, Hideaki*; Oyama, Yukiko*; Miyoshi, Shogo*; Yamaguchi, Shu*
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 600(1), p.319 - 321, 2009/02
Times Cited Count:22 Percentile:80.29(Instruments & Instrumentation)The neutron powder diffraction data of the apatite-type La-silicate La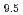 Si
Si O
O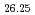 was measured at 10 K and the Rietveld refinement on the basis of hexagonal P6
was measured at 10 K and the Rietveld refinement on the basis of hexagonal P6 /m was successfully carried out. The obtained cell parameters were
/m was successfully carried out. The obtained cell parameters were  =0.971297(7) nm, and
=0.971297(7) nm, and  = 0.717950(6) nm. On the Rietveld refinement supported by maximum entropy method, the interstitial oxygen positions show randomly distribution around La2 site, and they may give the driving-force of high ionic conductivity to the main ionic conduction site O4.
= 0.717950(6) nm. On the Rietveld refinement supported by maximum entropy method, the interstitial oxygen positions show randomly distribution around La2 site, and they may give the driving-force of high ionic conductivity to the main ionic conduction site O4.